Robust Linear Models¶
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
[2]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import statsmodels.api as sm
Estimation¶
Load data:
[3]:
data = sm.datasets.stackloss.load()
data.exog = sm.add_constant(data.exog)
Huber’s T norm with the (default) median absolute deviation scaling
[4]:
huber_t = sm.RLM(data.endog, data.exog, M=sm.robust.norms.HuberT())
hub_results = huber_t.fit()
print(hub_results.params)
print(hub_results.bse)
print(
hub_results.summary(
yname="y", xname=["var_%d" % i for i in range(len(hub_results.params))]
)
)
const -41.026498
AIRFLOW 0.829384
WATERTEMP 0.926066
ACIDCONC -0.127847
dtype: float64
const 9.791899
AIRFLOW 0.111005
WATERTEMP 0.302930
ACIDCONC 0.128650
dtype: float64
Robust linear Model Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: y No. Observations: 21
Model: RLM Df Residuals: 17
Method: IRLS Df Model: 3
Norm: HuberT
Scale Est.: mad
Cov Type: H1
Date: Tue, 13 Jan 2026
Time: 23:44:51
No. Iterations: 19
==============================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
var_0 -41.0265 9.792 -4.190 0.000 -60.218 -21.835
var_1 0.8294 0.111 7.472 0.000 0.612 1.047
var_2 0.9261 0.303 3.057 0.002 0.332 1.520
var_3 -0.1278 0.129 -0.994 0.320 -0.380 0.124
==============================================================================
If the model instance has been used for another fit with different fit parameters, then the fit options might not be the correct ones anymore .
Huber’s T norm with ‘H2’ covariance matrix
[5]:
hub_results2 = huber_t.fit(cov="H2")
print(hub_results2.params)
print(hub_results2.bse)
const -41.026498
AIRFLOW 0.829384
WATERTEMP 0.926066
ACIDCONC -0.127847
dtype: float64
const 9.089504
AIRFLOW 0.119460
WATERTEMP 0.322355
ACIDCONC 0.117963
dtype: float64
Andrew’s Wave norm with Huber’s Proposal 2 scaling and ‘H3’ covariance matrix
[6]:
andrew_mod = sm.RLM(data.endog, data.exog, M=sm.robust.norms.AndrewWave())
andrew_results = andrew_mod.fit(scale_est=sm.robust.scale.HuberScale(), cov="H3")
print("Parameters: ", andrew_results.params)
Parameters: const -40.881796
AIRFLOW 0.792761
WATERTEMP 1.048576
ACIDCONC -0.133609
dtype: float64
See help(sm.RLM.fit) for more options and module sm.robust.scale for scale options
Comparing OLS and RLM¶
Artificial data with outliers:
[7]:
nsample = 50
x1 = np.linspace(0, 20, nsample)
X = np.column_stack((x1, (x1 - 5) ** 2))
X = sm.add_constant(X)
sig = 0.3 # smaller error variance makes OLS<->RLM contrast bigger
beta = [5, 0.5, -0.0]
y_true2 = np.dot(X, beta)
y2 = y_true2 + sig * 1.0 * np.random.normal(size=nsample)
y2[[39, 41, 43, 45, 48]] -= 5 # add some outliers (10% of nsample)
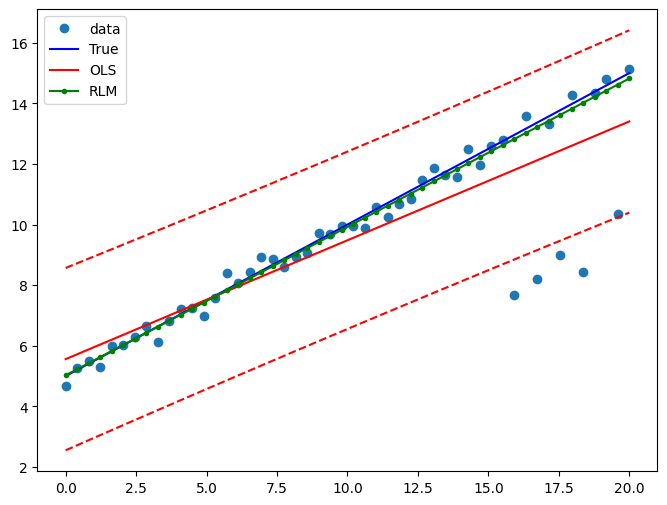
Example 1: quadratic function with linear truth¶
Note that the quadratic term in OLS regression will capture outlier effects.
[8]:
res = sm.OLS(y2, X).fit()
print(res.params)
print(res.bse)
print(res.predict())
[ 4.84798791 0.54482586 -0.01452255]
[0.46607995 0.07195645 0.00636704]
[ 4.48492409 4.7641583 5.03855367 5.30811021 5.57282791 5.83270678
6.08774682 6.33794802 6.58331038 6.82383391 7.05951861 7.29036447
7.5163715 7.73753969 7.95386904 8.16535957 8.37201125 8.57382411
8.77079812 8.96293331 9.15022966 9.33268717 9.51030585 9.68308569
9.8510267 10.01412887 10.17239221 10.32581672 10.47440239 10.61814922
10.75705723 10.89112639 11.02035672 11.14474822 11.26430088 11.37901471
11.4888897 11.59392586 11.69412318 11.78948167 11.88000132 11.96568214
12.04652412 12.12252727 12.19369158 12.26001706 12.32150371 12.37815152
12.42996049 12.47693063]
Estimate RLM:
[9]:
resrlm = sm.RLM(y2, X).fit()
print(resrlm.params)
print(resrlm.bse)
[ 4.79204715e+00 5.23967587e-01 -2.86673769e-03]
[0.14217485 0.02194988 0.00194223]
Draw a plot to compare OLS estimates to the robust estimates:
[10]:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(x1, y2, "o", label="data")
ax.plot(x1, y_true2, "b-", label="True")
pred_ols = res.get_prediction()
iv_l = pred_ols.summary_frame()["obs_ci_lower"]
iv_u = pred_ols.summary_frame()["obs_ci_upper"]
ax.plot(x1, res.fittedvalues, "r-", label="OLS")
ax.plot(x1, iv_u, "r--")
ax.plot(x1, iv_l, "r--")
ax.plot(x1, resrlm.fittedvalues, "g.-", label="RLM")
ax.legend(loc="best")
[10]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f5098da8970>
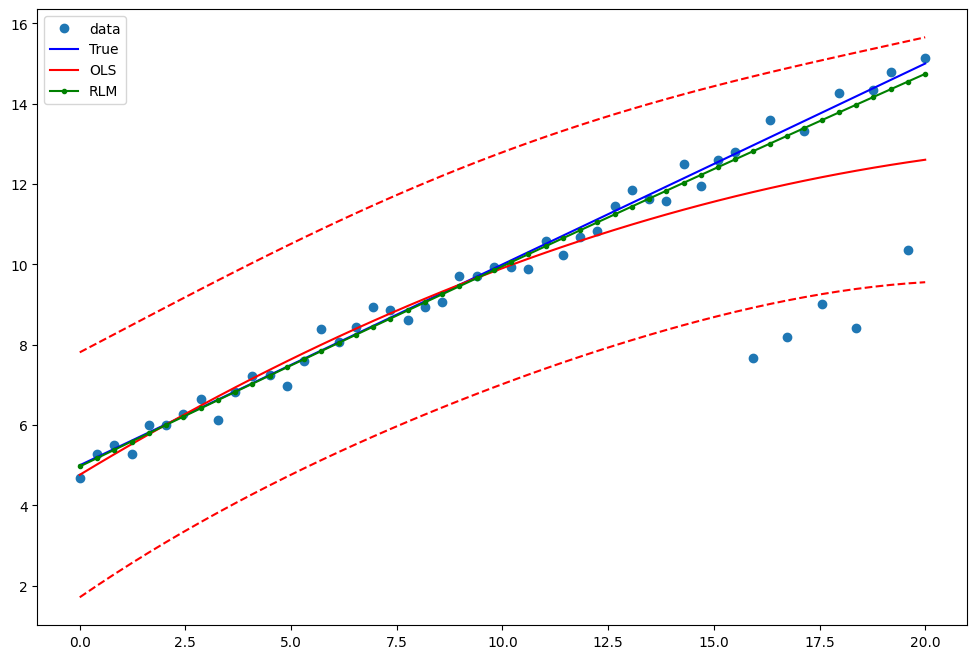
Example 2: linear function with linear truth¶
Fit a new OLS model using only the linear term and the constant:
[11]:
X2 = X[:, [0, 1]]
res2 = sm.OLS(y2, X2).fit()
print(res2.params)
print(res2.bse)
[5.4333357 0.39960033]
[0.40573901 0.03496011]
Estimate RLM:
[12]:
resrlm2 = sm.RLM(y2, X2).fit()
print(resrlm2.params)
print(resrlm2.bse)
[4.89499446 0.49690266]
[0.11293958 0.00973133]
Draw a plot to compare OLS estimates to the robust estimates:
[13]:
pred_ols = res2.get_prediction()
iv_l = pred_ols.summary_frame()["obs_ci_lower"]
iv_u = pred_ols.summary_frame()["obs_ci_upper"]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.plot(x1, y2, "o", label="data")
ax.plot(x1, y_true2, "b-", label="True")
ax.plot(x1, res2.fittedvalues, "r-", label="OLS")
ax.plot(x1, iv_u, "r--")
ax.plot(x1, iv_l, "r--")
ax.plot(x1, resrlm2.fittedvalues, "g.-", label="RLM")
legend = ax.legend(loc="best")